Contents
- 1 Navigating Through the Complexities of Prostate Inflammation
- 2 Prof. Aécio D’Silva, Ph.D. AquaUniversity
- 3 Prostatitis is a common yet often misunderstood condition affecting the prostate gland. This guide aims to demystify prostatitis by exploring its classifications, symptoms, triggers, and treatment options.
- 4 What is?
- 5 Classifications: It is classified into four main types
- 6 Symptoms and Signs
- 7
- 8 What Triggers Prostatitis?
- 9 Treatment:
- 10 Prognosis
- 11 Prevention
- 12 What lifestyle changes can help manage prostatitis symptoms?
- 13
- 14 Are there any specific exercises that can help with prostatitis?
- 15 How can I learn to do Kegel exercises correctly?
- 16 Are There Any Natural Treatments for Prostatitis?
- 17 How can stress reduction techniques complement natural treatments for prostatitis?
- 18 What specific stress reduction techniques are most effective for prostatitis?
Prof. Aécio D’Silva, Ph.D.
AquaUniversity
Prostatitis is a common yet often misunderstood condition affecting the prostate gland. This guide aims to demystify prostatitis by exploring its classifications, symptoms, triggers, and treatment options.
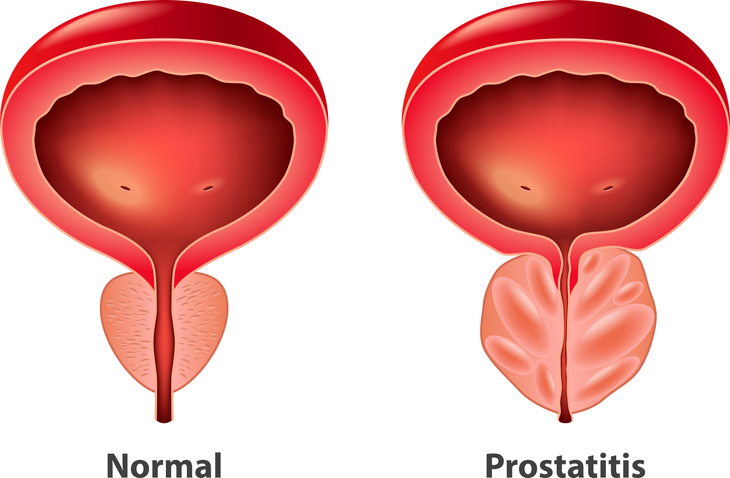
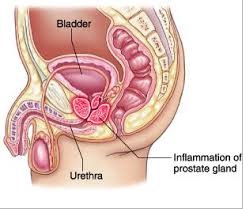
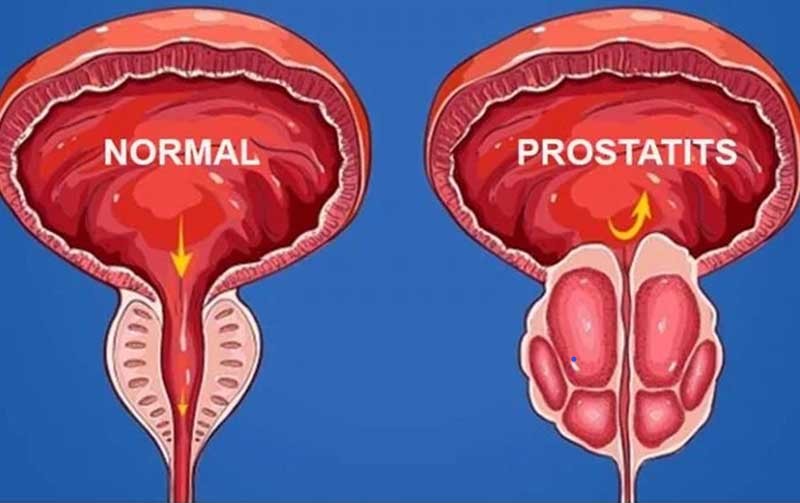
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland, a walnut-sized organ located below the bladder in men. It can lead to various urinary and pelvic symptoms, significantly impacting quality of life. Understanding prostatitis is crucial for effective management and treatment.
What is?
It refers to a spectrum of disorders that cause inflammation or infection of the prostate gland. It’s not a single condition but rather a group of conditions with varying causes and symptoms.
Classifications: It is classified into four main types
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: A sudden bacterial infection marked by severe symptoms.
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis: A recurrent bacterial infection with persistent symptoms.
- Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS): The most common form, characterized by chronic pelvic pain without a clear infection.
- Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate without symptoms.
Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms can vary but often include:
- Painful or burning urination
- Difficulty urinating
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Pelvic, abdominal, or lower back pain
- Painful ejaculation
- Blood in urine or semen.
What Triggers Prostatitis?
It can be triggered by:
- Bacterial infections
- Urine leakage into the prostate gland
- Nerve damage from surgery or trauma
- Bladder or urinary tract infections
- Pelvic trauma or injury.
Treatment:
Treatment depends on the type of prostatitis:
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Acute bacterial prostatitis will be treated with antibiotics. The medication time is at least two weeks, with the possibility of 4 or 12 weeks. It is very important that the patient continues to take the antibiotics prescribed by the doctor even if the symptoms have disappeared. Bacteria in the prostate can be difficult to eliminate and kill. Even if some remain alive, they can grow, and symptoms may return. You can also use other types of medications to relieve pain and bothersome symptoms. Medications called alpha-blockers relax the muscles of the bladder and prostate, which can make it easier for the patient to urinate. Anti-inflammatories may also be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis: Treated with longer courses of antibiotics.
- CPPS: Managed with a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
- Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis: Generally, does not require treatment
Prognosis
Acute prostatitis, when treated with appropriate antibiotics and at the correct time, right at the onset of symptoms, usually results in a complete cure without leaving sequelae. On the other hand, chronic prostatitis is more challenging to treat and requires more frequent check-ups. In cases of persistence of infectious factors, new courses of antibiotics should be administered. Despite all efforts, many patients end up suffering from changes in fertility – a feared complication of the disease.
Prevention
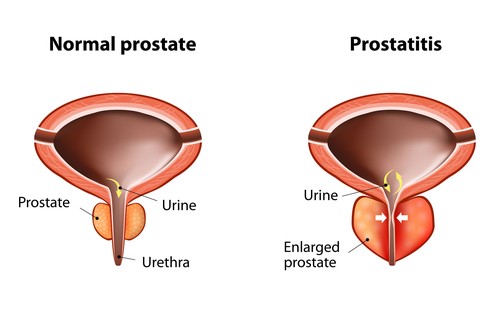
Simple hygiene habits can be key to preventing prostatitis. Every man after the age of 40/50 should visit his urologist regularly to evaluate the prostate and check for the presence of possible cancerous foci and/or the growth of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The latter is the main cause of prostate enlargement, which can lead to the narrowing of the urethral canal and, as a consequence, urine residue after urination. Stagnant urine in the bladder is an excellent culture medium for infection.
What lifestyle changes can help manage prostatitis symptoms?
Managing symptoms can often be aided by making certain lifestyle changes. Here are some recommended adjustments:
- Warm Baths: Soaking in a warm bath, also known as a sitz bath, can help relieve discomfort and pain.
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoiding alcohol, caffeine, and acidic or spicy foods can help reduce bladder irritation and discomfort.
- Hydration: Drinking sufficient fluids that are non-caffeinated can help flush out the urinary tract and reduce symptoms.
- Cushioning: Sitting on a soft cushion or a special inflated pillow can help reduce pressure on the prostate, which may alleviate pain.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
- Stress Reduction: Practicing relaxation techniques and reducing stress can also have a positive impact on managing prostatitis symptoms.
These changes can contribute to symptom relief and improve the quality of life for those dealing with it.
Are there any specific exercises that can help with prostatitis?
Yes, there are specific exercises that can help manage symptoms. These include:
- Kegel Exercises: These are designed to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which can help control urination and reduce symptoms related to prostatitis.
- Aerobic Exercises: Activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, and tennis can improve overall health and may help alleviate its symptoms. Regular physical activity is beneficial for managing chronic pelvic pain syndrome/chronic prostatitis.
- Stretching and Non-Aerobic Exercises: Exercises such as leg lifts, sit-ups, and general stretching can also be part of a comprehensive exercise program for men with prostatitis.
It’s important to note that before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have prostatitis or other health concerns, you should consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that the exercises are safe and appropriate for your specific condition.
How can I learn to do Kegel exercises correctly?
Learning to do Kegel exercises correctly involves several steps to ensure you’re targeting the right muscles and performing the exercises effectively:
- Identify the Pelvic Floor Muscles: The first step is to identify your pelvic floor muscles, which can be done by trying to stop your urine flow midstream. This is only for the purpose of identifying the muscles; you shouldn’t regularly stop urination this way as it can be harmful.
- Perfect the Technique: Once you’ve identified the pelvic floor muscles, empty your bladder, and sit or lie down. Tighten your pelvic floor muscles, hold the contraction for three seconds, and then relax for three seconds. Ensure that you’re not tightening your abdominal, thigh, or buttocks muscles during the exercise.
- Maintain Your Focus: For the best results, focus on tightening only your pelvic floor muscles. Be sure to breathe freely during the exercises and maintain a consistent routine.
- Repeat the Exercises: Aim to do at least three sets of 10 repetitions a day. As your muscles get stronger, you can gradually increase the duration of the contractions and the number of repetitions.
Remember, consistency is key. It may take several weeks to see improvement, and maintenance exercises are important even after you’ve achieved your initial goals. If you’re having trouble doing Kegel exercises, don’t hesitate to ask for help from your doctor or a pelvic floor therapist.
Are There Any Natural Treatments for Prostatitis?
Yes, several natural treatments can help manage its symptoms. These include:
- Warm Baths: Taking warm baths can help relieve pelvic discomfort and pain.
- Dietary Changes: Avoiding alcohol, caffeine, and spicy or acidic foods can reduce bladder irritation.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the bladder.
- Herbal Remedies: Supplements like saw palmetto and quercetin may help with urinary symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Techniques like myofascial trigger point release and biofeedback can aid in managing chronic pelvic pain associated with prostatitis.
How can stress reduction techniques complement natural treatments for prostatitis?
Stress reduction techniques can significantly complement natural treatments by addressing the psychological and emotional factors that may contribute to the condition. Here’s how they can help:
- Reducing Muscle Tension: Stress can lead to increased muscle tension, including the pelvic floor muscles. Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help relax these muscles, potentially alleviating symptoms of prostatitis.
- Improving Immune Response: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system. Stress management through relaxation techniques can bolster immune function, which is important in fighting infections that may cause or exacerbate prostatitis.
- Enhancing Overall Well-being: Stress reduction can improve overall well-being and quality of life, which can be particularly beneficial for those dealing with chronic conditions like prostatitis.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT and other similar therapies can help individuals develop coping strategies to manage stress, which may reduce the frequency and severity of prostatitis symptoms.
Incorporating stress reduction techniques into a treatment plan for prostatitis can provide a more holistic approach to managing the condition.
What specific stress reduction techniques are most effective for prostatitis?
Several stress reduction techniques have been found effective for managing it, particularly chronic /chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), which can be exacerbated by stress. These techniques include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress and anxiety, which may alleviate symptoms of prostatitis.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Gentle exercises such as yoga and tai chi can promote relaxation, reduce stress, and may help relieve some symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help manage stress and improve overall well-being, which is beneficial for prostatitis sufferers.
- Biofeedback: This technique helps individuals gain control over certain bodily processes, which can reduce tension and pain.
- Therapy: Talking to a therapist or counselor can help address the psychological aspects of chronic pain and stress management.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing can help calm the nervous system and reduce the stress response, which might be helpful for prostatitis patients.
Incorporating these stress reduction techniques into your daily routine may help manage the symptoms of prostatitis. Remember, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment. The information provided on this website is for educational or informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice or consultation with healthcare professionals.
In summary, Prostatitis is a multifaceted condition that requires a nuanced approach to diagnosis and treatment. Understanding its classifications, symptoms, triggers, and treatment options is essential for those affected by this condition. With proper medical care, individuals can manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.
References
[1] https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2010/0815/p397.html.
[2] https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15319-prostatitis
[3] https://www.healthinaging.org/a-z-topic/prostate-diseases/lifestyle.
[4] https://www.webmd.com/men/prostatitis.
[5] https://www.imedix.com/diseases/prostatitis.
[6] https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/exercise-and-chronic-prostatitis-2011042614718
[7] https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/mens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises-for-men/art-20045074
[8] https://prostate.net/stress-management-treating-prostatitis/.