Gene-Based Treatment for Vitiligo: Pioneering Advances in Restoring Skin Pigmentation.
Prof. Aécio D’Silva, Ph.D
AquaUniversity
Embracing a brighter future for vitiligo patients through cutting-edge gene-based treatments
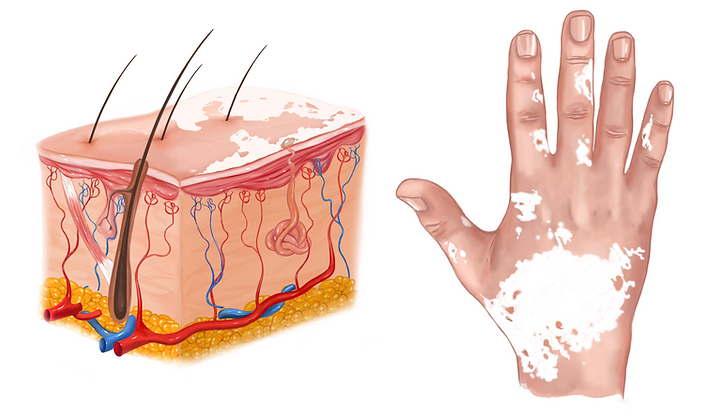
Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes patches of skin to lose pigment or color. Between 35 and 70 million people suffer from vitiligo globally. The cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it may be related to immune system changes, genetic factors, stress, or sun exposure. While the condition is not life-threatening, its impact on a person’s self-esteem and quality of life can be profound. Over the years, medical advancements have explored various treatment modalities, but gene-based therapies are emerging as a promising frontier. In this blog, we delve into the revolutionary potential of gene-based treatments for vitiligo and their potential to restore pigmentation, offering new hope to those affected by this condition.
Vitiligo – The Promise of Gene-Based Treatment
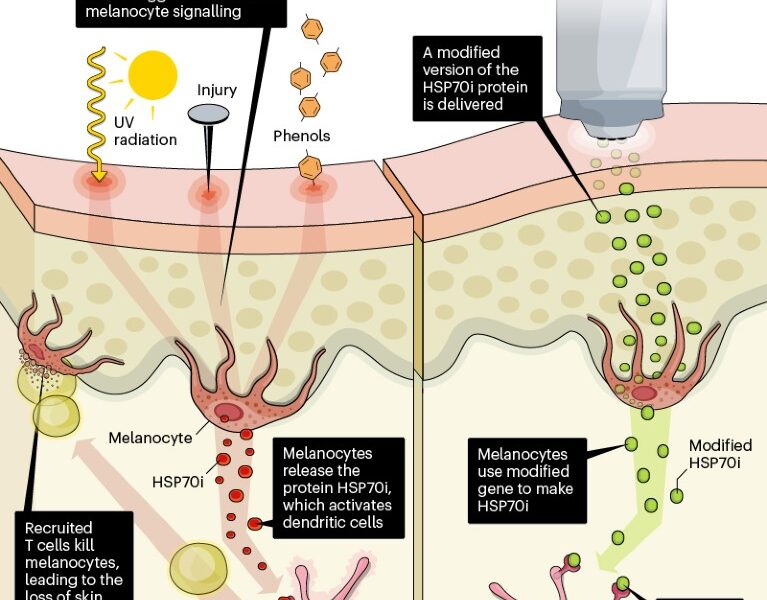
As our understanding of genetics expands, so does our ability to harness the power of genes for therapeutic purposes. Gene-based treatments for vitiligo focus on targeting specific genes and signaling pathways involved in the disease progression. This approach aims to restore the function of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells that are either destroyed or rendered dysfunctional in vitiligo patients.
One promising avenue of gene-based treatment is gene therapy, which involves delivering functional copies of genes to the patient’s skin cells using viral vectors or other delivery mechanisms. These genes can restore the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, thus reversing the depigmentation characteristic of this autoimmune disorder. Gene therapy offers the potential for long-lasting and potentially permanent results, making it an exciting prospect for individuals seeking an effective and durable solution for vitiligo.
Targeted Gene Editing Techniques
In addition to gene therapy, targeted gene editing techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 hold significant promise in treating vitiligo. CRISPR-Cas9 allows scientists to precisely edit the DNA sequence of specific genes, enabling them to correct genetic mutations or modify gene expression. By targeting genes associated with melanocyte function, researchers hope to enhance the production of melanin and restore pigmentation in vitiligo-affected skin.
While gene editing approaches are still in the early stages of development, preclinical studies have demonstrated encouraging results. These techniques have the potential to revolutionize vitiligo treatment by directly addressing the underlying genetic factors that contribute to the disease. However, more research is needed to ensure the safety, efficacy, and long-term effects of gene editing therapies before they can be widely implemented in clinical settings.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As with any emerging field, gene-based treatments for this autoimmune disorder face several challenges and ethical considerations. One significant challenge is the efficient delivery of therapeutic genes or gene-editing tools to the target cells in the skin. Ensuring precise and targeted delivery while minimizing off-target effects remains a key focus of ongoing research.
Ethical considerations surrounding gene-based treatments also demand careful evaluation. Issues such as the informed consent process, potential unforeseen side effects, and equitable access to these innovative therapies need to be addressed to ensure that patients are well-informed, protected, and empowered in their treatment choices. Striking a balance between the rapid progress of science and the responsible application of these technologies is essential for the successful integration of gene-based treatments into clinical practice.
A Future of Hope
While gene-based treatments for this autoimmune disorder are still in the experimental stages, the progress made thus far is undeniably promising. With continued research and innovation, there is genuine hope for developing effective and safe therapies that can restore pigmentation and transform the lives of those affected by vitiligo.
By addressing the underlying genetic factors of this autoimmune disorder, gene-based treatments hold the potential to provide long-lasting solutions, reduce the burden of daily treatments, and offer individuals the opportunity to regain their self-confidence and embrace their natural skin color.
To conclude, gene-based treatments are at the forefront of medical breakthroughs for this autoimmune disorder, ushering in a new era of targeted therapies. The potential to restore pigmentation by manipulating genes and gene expression brings renewed hope to individuals living with vitiligo. While challenges remain, the dedication of researchers and the resilient spirit of the vitiligo community propel us toward a future where the restoration of skin pigmentation becomes a reality.
References:
- Temprian Therapeutics (https://www.tempriantherapeutics.com/ –
- https://www.facebook.com/TemprianTherapeutics).
- Vitiligo: MedlinePlus Genetics: https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/vitiligo/
- Is Vitiligo Genetic? – Verywell Health: https://www.verywellhealth.com/is-vitiligo-genetic-5211682