Contents
- 1
- 2 Understanding How Immunotherapy Works and Its Benefits
- 3 Prof. Aécio D’Silva, Ph.D AquaUniversity
- 4 Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. As a researcher involved in applied genetics, I have been closely following the admirable advances that are happening in immunotherapy. This revolutionary approach has shown remarkable results in treating various types of cancer and is quickly becoming a popular option for cancer patients.
- 5 Immunotherapy Treatment Explained – How Does Immunotherapy Work?
- 6 Immunotherapy Treatment Explained – Benefits of Immunotherapy
- 7 Immunotherapy Treatment Explained – Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy?
- 8
- 9 Potential Side Effects of Immunotherapy
Understanding How Immunotherapy Works and Its Benefits
Prof. Aécio D’Silva, Ph.D
AquaUniversity
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. As a researcher involved in applied genetics, I have been closely following the admirable advances that are happening in immunotherapy. This revolutionary approach has shown remarkable results in treating various types of cancer and is quickly becoming a popular option for cancer patients.
Immunotherapy Treatment Explained – Cancer is one of the deadliest diseases in the world, affecting millions of people every year. Traditionally, cancer treatment involves surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. However, these treatments can cause several side effects and may not always be effective. In recent years, a new type of cancer treatment has emerged that harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer cells. This treatment is called immunotherapy and has shown promising results in treating various types of cancer.
Immunotherapy Treatment Explained – How Does Immunotherapy Work?
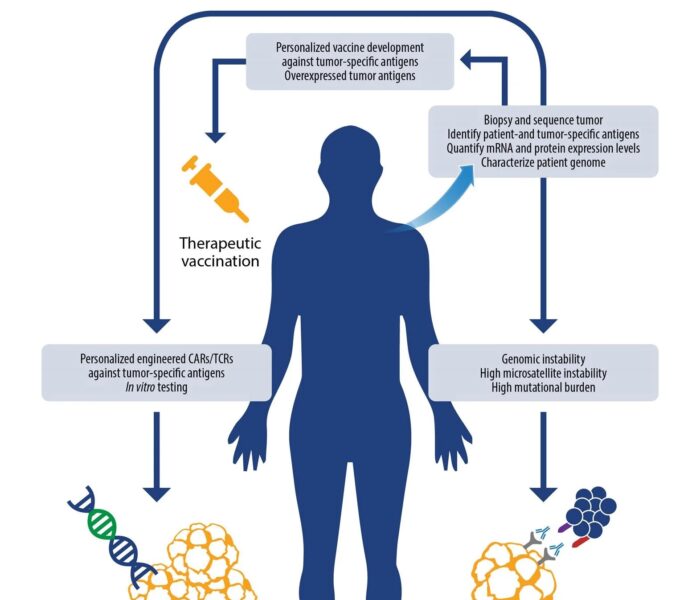
Immunotherapy works by boosting the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Cancer cells can often go undetected by the immune system as they are similar to healthy cells. Immunotherapy helps the immune system recognize cancer cells as foreign and attack them.
There are several types of immunotherapy treatments, including monoclonal antibodies, checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines, and adoptive cell transfer. Each treatment works differently, but they all aim to boost the immune system to fight cancer cells.
Immunotherapy Treatment Explained – Benefits of Immunotherapy
One of the main benefits of immunotherapy is that it has fewer side effects than traditional cancer treatments. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can cause significant damage to healthy cells, leading to side effects such as nausea, hair loss, and fatigue. Immunotherapy, on the other hand, targets only cancer cells, resulting in fewer side effects.
Another benefit of immunotherapy is that it can be more effective than traditional cancer treatments in some cases. For example, checkpoint inhibitors have shown remarkable results in treating melanoma, lung cancer, and bladder cancer. In clinical trials, these treatments have been able to shrink tumors or even eliminate them altogether.
Immunotherapy Treatment Explained – Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy can benefit many cancer patients, but it may not be the best option for everyone. Immunotherapy is generally more effective for patients with advanced cancer who have not responded to traditional treatments. Patients with certain types of cancer, such as melanoma, lung cancer, and bladder cancer, have shown remarkable results with immunotherapy.
However, not all cancer patients will respond to immunotherapy. Doctors will determine if a patient is a good candidate for immunotherapy based on several factors, including the type of cancer, the stage of cancer, and the patient’s overall health.
Potential Side Effects of Immunotherapy
While immunotherapy has fewer side effects than traditional cancer treatments, it can still cause some side effects. The most common side effects include fatigue, fever, and chills. Some patients may also experience skin reactions, such as rashes and itchiness. In rare cases, immunotherapy can cause more severe side effects, such as lung inflammation and heart problems.
It’s important for patients to discuss the potential side effects with their doctor before starting immunotherapy. Doctors can monitor patients closely and provide treatment if necessary.
Concluding, Immunotherapy is a revolutionary approach to cancer treatment that has shown remarkable results in treating various types of cancer. This treatment harnesses the power of the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. While immunotherapy has fewer side effects than traditional cancer treatments, it may not be the best option for everyone. Patients should discuss the potential benefits and risks with their doctor before starting immunotherapy.